Well, thats where enterprise architecture comes into play. In simple terms, enterprise architecture is like the master blueprint of an organization. Its a framework that is defines that are strategic different components, such as processes, technologies, and people, fit together to achieve business goals.Enterprise architecture provides a clear understanding of an state that is organizations is current guides its future direction. It helps identify inefficiencies, streamline operations, and ensure that all the right parts that are moving harmoniously. Think of it the adhesive that holds everything together.
You may be thinking, Are there frameworks that are specific enterprise architecture? Absolutely! Several frameworks, like TOGAF and Zachman, provide a approach that is structured developing and enterprise architecture that is implementing. In a nutshell, enterprise architecture is the sauce that is secret empowers organizations to navigate complexity, drive efficiency, and build a foundation that is solid success.�
What Is Enterprise Architecture?

Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a discipline that focuses on designing and managing an organizations structure that is operation that is overall. It provides a blueprint and framework for aligning business strategy, processes, information systems, and technology infrastructure to achieve the organizations goals and objectives.
EA takes a approach that is holistic considering various dimensions of an enterprise, including its business architecture, information architecture, application architecture, and technology architecture.� These dimensions are interconnected and interdependent, and EA helps ensure their alignment and integration.
The goals of Enterprise Architecture include:
Alignment: Ensuring business strategies, processes, and technology investments align with the organizations goals and objectives.
Integration: Facilitating the integration that is interoperability that is seamless of processes, applications, and data across the organization.
Efficiency: Optimizing the use of resources, reducing duplication, and improving efficiency that is operational.
Agility: enabling the organization to respond quickly and effectively to changes in the business environment, technology advancements, and market dynamics.
Risk Management: Identifying and risks that are managing with technology investments, data security, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key Components of Enterprise Architecture
The critical components of Enterprise Architecture include:
Business Architecture: This component defines the organizations business strategy, goals, processes, and structure. It identifies the continuing business that is critical, value streams and how they are linked to achieve business objectives.
Information Architecture: Information architecture focuses on managing and data that are organizing within the organization. It involves defining data models, information flows, data storage, data governance, and information that is ensuring, integrity, and security.
Application Architecture: Application architecture deals with software and designing that is integrating to support business processes. It includes defining the application portfolio, application interfaces, and integration patterns and application and selecting that is managing and technologies.
Technology Architecture: Technology architecture encompasses the hardware, software, network infrastructure, and technology platforms that support the organizations operations. It includes defining the technology stack, standards, and security measures and ensuring the technology infrastructures scalability, reliability, and performance.
Benefits of Enterprise Architecture
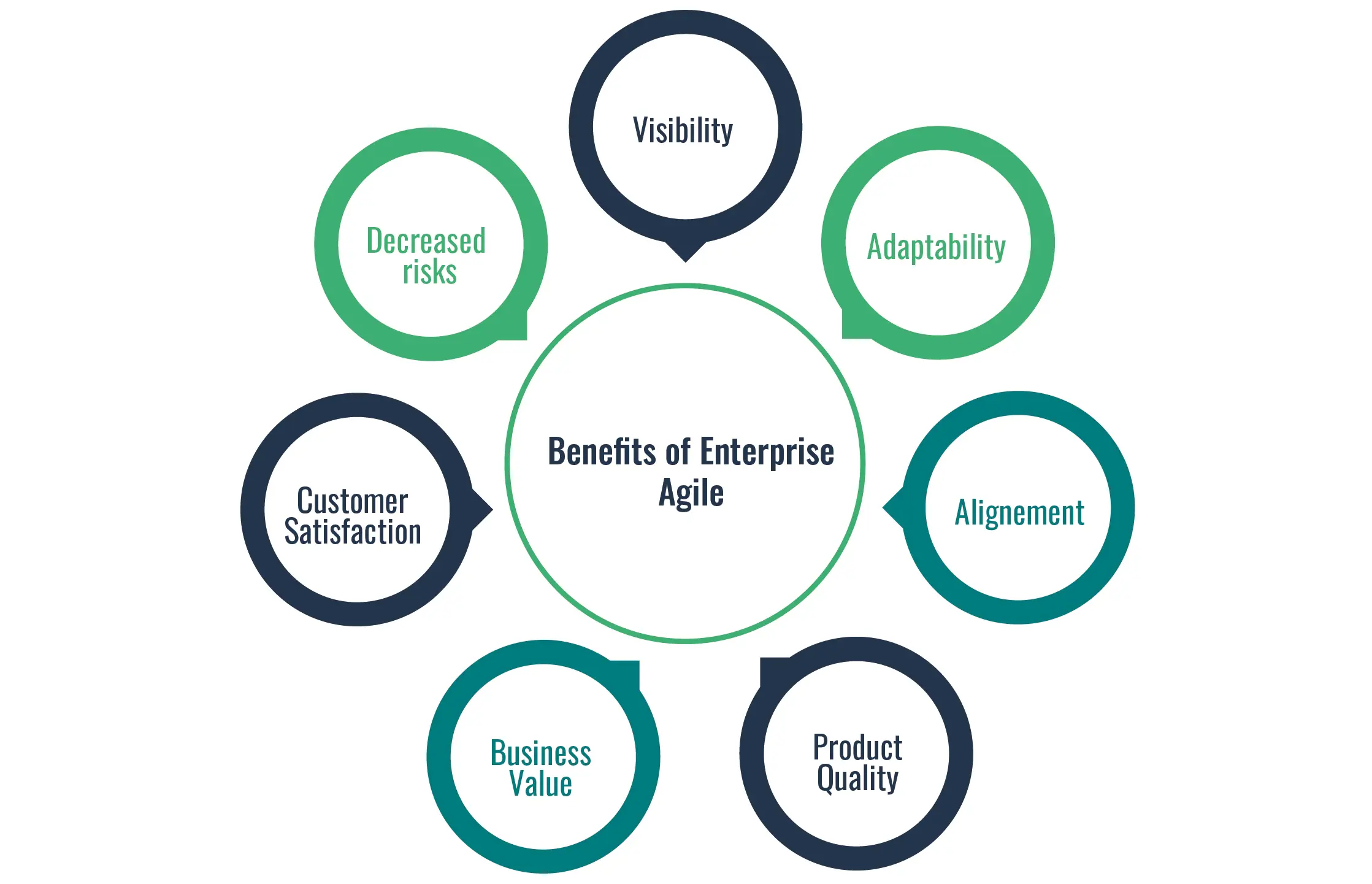
Enterprise Architecture (EA) offers benefits that are several organizations. Here are some advantages that are key
Alignment of Business and IT: Enterprise architecture helps align the organizations business strategies and goals with its IT capabilities. It ensures that technology investments and initiatives are closely tied to business objectives, facilitating better decision-making and resource allocation.
Improved Efficiency and Effectiveness: By analyzing and business that is optimizing, Enterprise architecture identifies opportunities for streamlining operations, eliminating redundancies, and efficiency that is improving. It enables organizations to leverage technology effectively to automate processes, reduce effort that is manual and enhance productivity that is overall.
Enhanced Agility and Flexibility: Enterprise architecture enables organizations to adapt quickly to business that is changing, market conditions, and technologies that are emerging. It promotes agility by providing a approach that is structured managing and integrating technologies that are new applications, and systems, allowing organizations to respond rapidly to market opportunities and challenges.
Reduced Complexity and Cost: Through rationalization and standardization of technology infrastructure and applications, Enterprise architecture helps reduce complexity and eliminate duplication. This simplification leads to cost savings in terms of reduced maintenance, support, and licensing expenses.
Risk Management and Compliance: Enterprise architecture helps identify and mitigate technology, data security, and compliance that is regulatory. Establishing standards, controls, and governance mechanisms ensures that technology implementations adhere to industry best practices and requirements that are regulatory.
Support for Innovation and Digital Transformation: Enterprise architecture provides a foundation that is innovation that is solid digital transformation initiatives. It enables organizations to leverage emerging technologies like cloud computing, big data analytics, and intelligence that is artificial drive innovation, improve customer experiences, and gain a edge that is competitive.
Enterprise Architecture Frameworks and Standards
There are several widely recognized Enterprise Architecture (EA) frameworks and standards that organizations can use as reference models and guidelines for implementing EA practices. Here are some frameworks that are popular standards:
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF): TOGAF is one of the most widely adopted EA frameworks. It provides a approach that is comprehensive designing, planning, implementing, and enterprise architecture that is governing. TOGAF offers a methodology that is structured best practices, and a framework for developing architecture artifacts.
Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework (FEAF): U.S. government that is employ FEAF that is federal. It provides a approach that is standardized developing and implementing enterprise architecture within the government that is federal. FEAF emphasizes the alignment of business, data, applications, and technology architecture to support agency missions and goals.
Zachman Framework: The Zachman Framework is a widely recognized and framework that is industry-agnotic provides a approach that is structured organizing and describing enterprise architecture artifacts. It defines a framework that is matrix-based six perspectives, including what, how, where, who, when, and why, to capture the different dimensions of enterprise architecture.
The Gartner Enterprise Architecture Framework: Developed by Gartner, this framework guides creating and enterprise that is using to drive business outcomes. It focuses on developing a roadmap that is integrating that is strategic and IT, and enabling digital transformation initiatives.
ISO/IEC 42010: ISO/IEC 42010 is an standard that is architecture that is international, providing principles and guidelines for architectural documentation and communication. It emphasizes the importance of stakeholders, viewpoints, and the use of architecture frameworks to describe and analyze system architectures.
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL is a set of recommended practices IT services for IT service management that provides a approach that is structured managing. A range is covered by it that is broad of processes. For instance, service design, service transition, and service operation.
Roles and Responsibilities in Enterprise Architecture

The Enterprise Architect is responsible for implementing and developing the enterprise architecture strategy that is organizations. Their duties include:
Maintaining and defining the enterprise architecture framework and methodologies.
Collaborating with stakeholders to understand business objectives and translate them into architectural requirements.
Designing and documenting the organizations current and target state architectures.
Identifying and technology that is assessing and evaluating their impact that is potential on enterprise.
Developing and standards that are implementing are architectural guidelines.
Providing guidance and support to project teams to ensure alignment with the enterprise architecture.
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the enterprise architecture and adjustments that are making necessary.
Skills and responsibilities of an Enterprise Architect may include:
Strong technical and business acumen.
Excellent analytical and skills that are problem-solving.
Broad knowledge of different domains that are architecturalbusiness, data, application, technology).
Ability to communicate complex concepts that are technical stakeholders that are non-technical.
Leadership and stakeholder management skills.
Knowledge of EA frameworks and methodologies (e.g., TOGAF).
Stakeholders and their involvement in enterprise architecture initiatives:
Enterprise architecture initiatives involve collaboration with various stakeholders across the organization. Some stakeholders that are key their involvement include:
Business Leaders: Business leaders provide strategic direction and priorities enterprise architecture that is influencing. They participate in defining business requirements, goals, and objectives that shape the architecture.
IT Teams: IT teams, including infrastructure, application development, and operations, collaborate closely with the enterprise architecture team. They provide technical expertise, implement decisions that are architectural and ensure alignment with IT strategies and standards.
Business Units: Business units are critical in defining requirements that are specific processes, and capabilities. They provide insights into business processes, identify areas for improvement, and solutions that are validate are architectural.
Data Management and Governance: Data management and governance teams ensure that data is managed effectively and aligned with the enterprise architecture. They collaborate to define data standards, quality requirements, and data integration strategies.
Security and Risk Management: Security and risk management teams work closely with the enterprise architecture team to ensure that security controls and risk mitigation measures get incorporated into the architecture.
Collaboration with other teams and departments (e.g., IT, business units):
Collaboration with other teams and departments is crucial for successful enterprise architecture initiatives. Here are some examples of collaboration areas:
IT Department: The enterprise architecture team collaborates with the IT department to ensure that technology investments align with the architecture and support business goals. They work together to define and implement technology standards, evaluate vendor solutions, and guide IT projects.
Business Units: Collaboration with business units involves understanding their needs that are specific processes, and goals. The enterprise architecture team works closely with business units to identify opportunities for process optimization, innovation, and aligning IT solutions with business requirements.
Project Teams: The enterprise architecture team collaborates with project teams to ensure that projects adhere to the architecture that is defined and standards. They provide guidance, review project designs, and support integrating solutions that are new the architecture that is existing.
Operations and Support: Collaboration with operations and support teams is essential for maintaining and evolving the enterprise architecture. The enterprise architecture team works with these teams to identify challenges that are operational optimize system performance, and address issues that are architectural the implementation and maintenance phases.
Effective collaboration with these united teams and departments ensures that the enterprise architecture is well-integrated, meets business needs, and is successfully maintained and implemented across the organization.